What are SEU agreements?
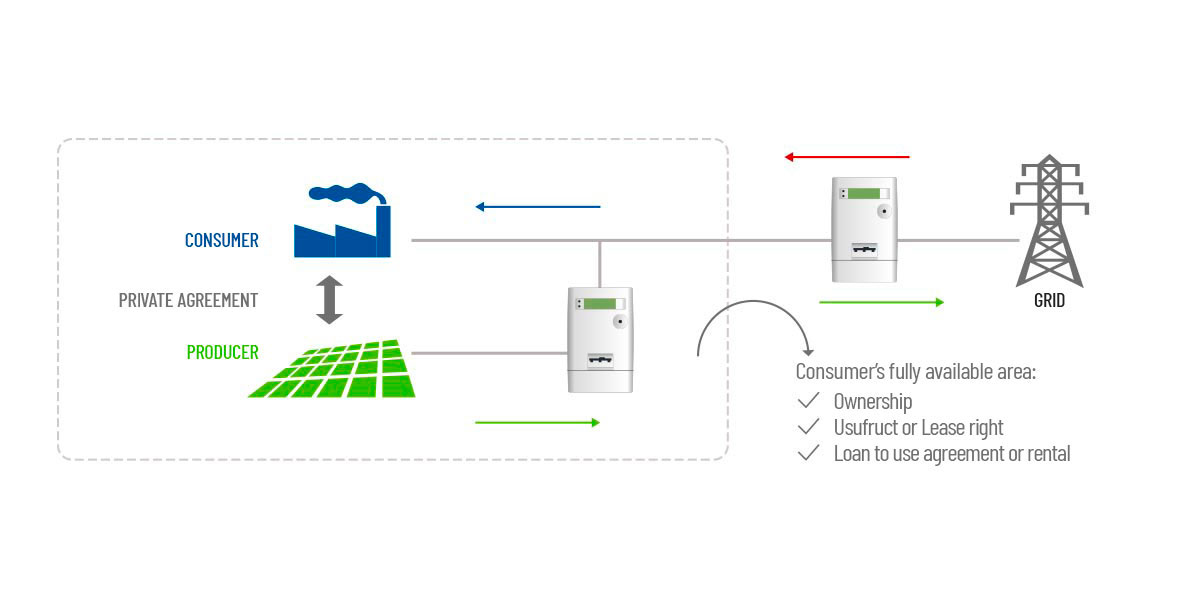
SEU (Italian acronym for Sistemi Efficienti di Utenza, Efficient Consumption Systems) are private agreements governing the sale of electric power between a Producer and a Consumer. The power plant is owned by the Producer and installed in areas close to the Consumer.
Who is the typical Client?
Typical clients are energy-intensive consumers, such as companies, production plants, logistic hubs, shopping centres.
How is it created and how does it work?
A SEU agreement foresees that the Producer installs and manages a photovoltaic plant on the rooftop of the Consumer’s plant (or on an adjacent area in his availability) so that the Consumer can absorb the energy produced through a direct and private connection to the photovoltaic system, bypassing the grid.
Consequently, the user avoids all duties and taxes charged in the electricity bill and pays only the energy expenses but at a much lower fare.
As a matter of fact I direct link between the supply and the demand of energy is created.
There can be mainly two types of SEU agreement, depending on the power of the plant:
- </= 500 kW. The Consumer buys from the Producer all the energy produced, absorbs immediately the share he needs and benefits from the exceeding share separately;
- >500 kW. The Consumer buys from the Producer only the amount of energy corresponding to his immediate needs.
In some cases we may take charge of removing asbestos and/ or renovating the roof.
What are the advantages for the Consumer?
- Immediate saving on the electricity bill
- Total saving starting from the transfer of ownership of the plant to the Consumer (*)
- A productive cycle with renewable sources that can be proposed to increasingly eco-conscious clients and stakeholders
- Enhancement of the Consumer’s real estate investment
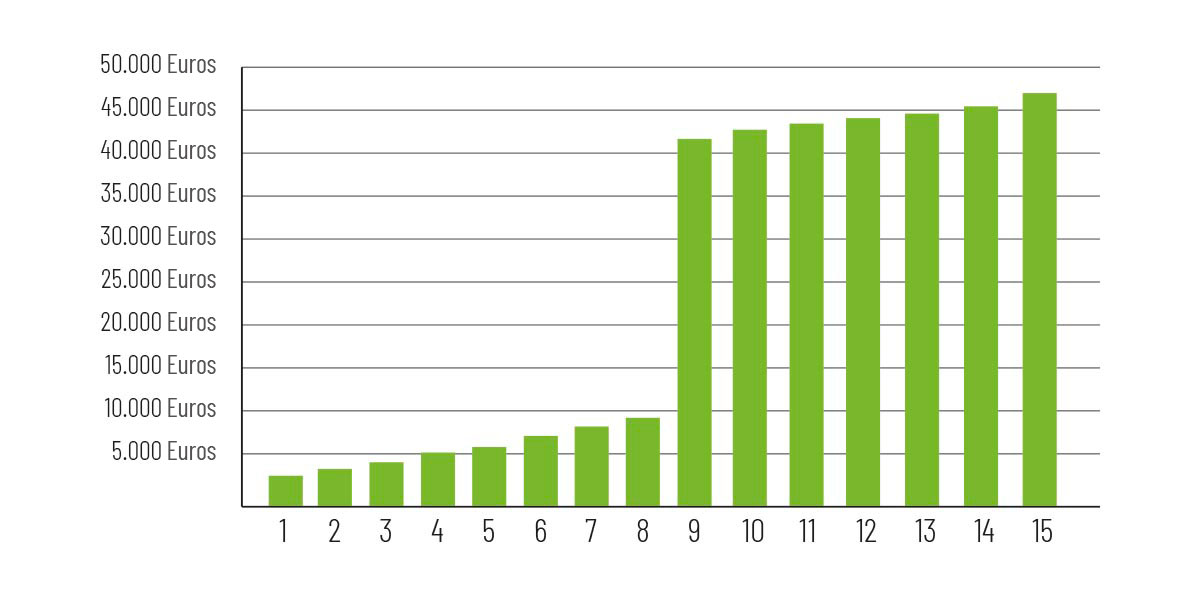
As an example, you may see below the benefits - over a period of 15 years - of a 200 kW photovoltaic plant with a hypothetical consumption of 300,000 kWh.
What are the advantages for the system and the environment?
- 0.5 kg of CO2 savings for each kWh of energy produced by a photovoltaic plant
- Implementation of distributed generation and grid relief from heavy energy loads
- Energy independence


